今后不妨先這樣:第一,以英文文獻為主,中文文獻僅擇其在本人看來較“有意思”的介紹;第二,以期刊為主,會議文獻次之;第三,以傳感原理大致分個類(僅僅大致而已,也可能按照原理,也可能按照被測量,看這段時間的文獻特點),讀起來也方便;第四,限于本人的研究領域,重點介紹物理量傳感器。
在光纖FP傳感器方面:
上海大學的T. Y. Wang等人提出了利用飛秒激光器在光纖內形成FP腔的方法(“Fiber-optic intrinsic Fabry-Perot interferometric sensors fabricated by femtosecond lasers,” in SPIE. vol. 8034, H. Xiao, et al., Eds., Bellingham: SPIE, 2011.)。與以前電子科大饒云江課題組(Y.-J. Rao, et al., “Micro Fabry-Perot interferometers in silica fibers machined by femtosecond laser,” Opt. Express, vol. 15, pp. 14123-14128, 2007.)報道方法不同,T. Y. Wang采用的是用透鏡將光束聚焦在纖芯,制作成兩個FP腔的“端面”。

圖1 飛秒激光器制作的FP腔“端面”
國防科大近期在兩個FBG形成FP腔的研究方面發表了一系列研究報道:S. L. Niu等人介紹了采用兩個FBG形成FP腔的方法(“Pico-strain measurement using optimised fibre Fabry-Perot sensor system with reference wavelength,” Electronics Letters, vol. 47, pp. 969-U47, Aug 2011.)。這種結構在上一期提到過,此文中達到1.5 pε的分辨率。
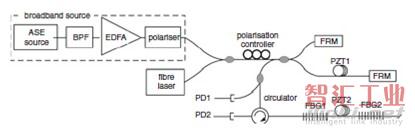
圖2 采用FBG對實現FP腔傳感器
W. Rao等報道了在FP干涉式傳感器中采用PGC的方法(“Phase-generated carrier demodulation scheme for fiber Fabry-Pérot interferometric sensor with high finesse,” Optical Engineering, vol. 50, p. 094401, 2011.),見圖3。上期曾提到哈爾濱工程大學的康崇報道了PGC算法在FP光纖水聽器方面的應用。此文與之不同的是,文中的FP腔采用PM光纖和兩個耦合器構成環形腔,以消除PIF,并具有較高的精細度。
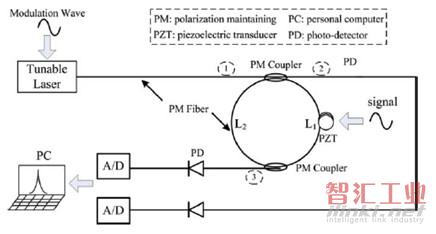
圖3 環形腔FP傳感器的系統圖
此外還有:牛嗣亮等,“光纖布拉格光柵及其構成的法布里-珀羅腔的相位譜特性研究,” 光學學報, vol. 31, p. 0806007, 2011.以及S. Niu, et al., “Fiber Fabry-Perot Hydrophone Based on Push-Pull Structure and Differential Detection,” Photonics Technology Letters, IEEE, vol. PP, pp. 1-1, 2011。
順便提一下,該課題組還報道了光纖水聽器4元陣的海試,(R. Wei, et al., “Seafloor exploration using a 4-element towed fiber optic hydrophone array,” in Electronics and Optoelectronics (ICEOE), 2011 International Conference on, 2011, pp. V2-359-V2-361.)。文中的光纖傳感器采用Michelson干涉式,3×3解調。
美國馬里蘭大學的H. Bae等人報道了在45度的光纖端面上制作FP腔的方法(“Investigation of miniature fiber optic surface-mountable Fabry-Perot pressure sensor built on 45 degrees angled fiber,” in Sensors and Smart Structures Technologies for Civil, Mechanical, and Aerospace Systems 2011. SPIE vol. 7981)。該傳感器可用來測溫度和壓力,但最大的優勢在于可方便地表面安裝。
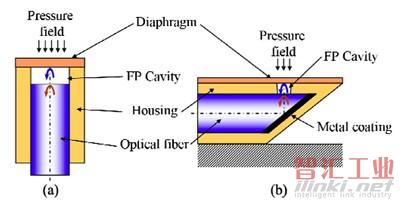
圖4 在光纖端面形成的FP傳感器
大連理工的H. Hao等提出了FP傳感器的頻分復用(Frequency division multiplexing of etrinsic Fabry-Perot interferometric (EFPI) optical fiber sensor. SPIE vol. 8191, 2011.)。就本人所知,這種方式上個世紀美國弗吉尼亞理工大學Anbo Wang課題組就提出過。文中最主要的圖之一Fig.2也沒有表達清楚,文中的S1、S2沒有標示出來。
在折射率傳感器方面:
北京理工大學的L. Jiang等人采用飛秒激光在光纖上刻蝕U型槽,從而形成微型的MZ干涉儀,用來進行折射率傳感(“Femtosecond laser fabricated all-optical fiber sensors with ultrahigh refractive index sensitivity: modeling and experiment,” Opt. Express, vol. 19, pp. 17591-17598, 2011.)。這種方法的靈敏度達到-3754.79 ± 44.24nm/RIU。
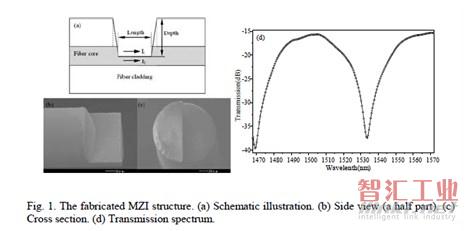
圖5 基于微型干涉儀的折射率傳感器
墨西哥的J. E. Antonio-Lopez等人提出了采用無芯光纖的液位傳感器(“Fiber-optic sensor for liquid level measurement,” Opt. Lett., vol. 36, pp. 3425-3427, 2011.),可同時進行液位和折射率的測量。
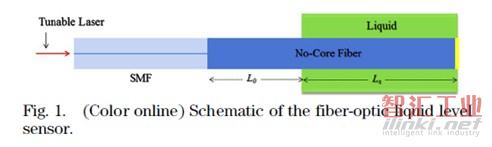
圖6 采用無芯光纖的液位傳感器
哈爾濱工程大學的Zhou等報道了基于非對稱雙芯光纖的折射率傳感器(“Asymmetrical Twin-Core Fiber Based Michelson Interferometer for Refractive Index Sensing,” JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, vol. 29, pp. 2985-2991, Oct 2011.)。通過化學腐蝕的方法去掉一段包層,使邊芯的基模有效折射率對外界敏感,靈敏度可達270 nm/RIU。
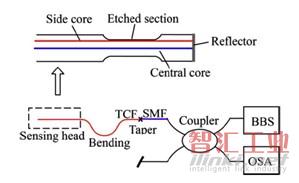
圖7 采用刻蝕方法的折射率傳感器
香港理工的M. Yang等提出了在FBG上打孔實現溫度和折射率同時測量的方法(“Fiber Bragg Grating With Micro-Holes for Simultaneous and Independent Refractive Index and Temperature Sensing,” Photonics Technology Letters, IEEE, vol. 23, pp. 1511-1513, 2011.)。通過透射譜上的峰值測量折射率,通過Bragg波長測量溫度。

圖8 光柵上打孔的傳感器
此外,馬來西亞的H. A. Rahman等報道了基于塑料光纖的鹽度傳感器(“Tapered Plastic Multimode Fiber Sensor For Salinity Detection,” Sensors and Actuators A: Physical.)。
香港理工的A. Q. Jian等報道了基于諧振光學隧道效應的折射率傳感器(“Liquid refractive index sensors using resonant optical tunneling effect for ultra-high sensitivity,” Sensors and Actuators a-Physical, vol. 169, pp. 347-351, Oct 2011.)。
在光纖光柵類傳感器及其解調和應用方面:
南開大學的Z. F. Wu等人提出了用CO2激光器在PCF上制作高質量的LPFG的方法,并通過理論和實驗驗證了LPFG是由LP01和LP11的模式耦合造成的(“Mechanism and characteristics of long period fiber gratings in simplified hollow-core photonic crystal fibers,” OPTICS EXPRESS, vol. 19, pp. 17344-17349, Aug 2011.)研究指出,模式耦合的機理是周期性的微彎。
加拿大渥太華大學的W. L. Liu等提出了線性啁啾FBG傳感器的實時解調方法(“Real-Time Interrogation of a Linearly Chirped Fiber Bragg Grating Sensor for Simultaneous Measurement of Strain and Temperature,” IEEE PHOTONICS TECHNOLOGY LETTERS, vol. 23, pp. 1340-1342, Sep 2011.)。該課題組還報道了基于干涉時序譜的快速高分辨率的FBG傳感器解調方法(C. Wang and J. P. Yao, “Ultrafast and Ultrahigh-Resolution Interrogation of a Fiber Bragg Grating Sensor Based on Interferometric Temporal Spectroscopy,” JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, vol. 29, pp. 2927-2933, Oct 2011.)。
北京交通大學的Y. Quan等提出了用FBG傳感器監測列車出軌的方法(Detecting the possibility of train derailment based on FBG sensor system. SPIE vol. 8191, 2011.),文中進行了一些分析,并在一個懸臂梁上進行了模擬實驗,沒有鋼軌試驗的結果。
中國計量大學的F. Zhang等給出了利用FBG傳感器進行高溫高壓管道監測的仿真分析(Optimized design and simulation of high temperature pressure pipeline strain monitoring with optical fiber sensing technology. SPIE vol. 8191, 2011.),文中并無實驗結果。
哈爾濱理工大學的J. Liu介紹了利用溫度調諧的DFB激光器進行FBG傳感器解調的方法(“FBG demodulation method based on DFB laser,” in Strategic Technology (IFOST), 2011 6th International Forum on, 2011, pp. 1207-1210.)
西北大學的J. H. Zhang等最近報道了兩種光纖加速度計,第一種是基于金屬波紋管(“Proposal of metal bellows-based fiber Bragg grating accelerometer,” Chinese Optics Letters, vol. 9, Sep 2011.),如圖9所示。典型的m-k系統,波紋管為彈性元件。另一種是基于彎張換能器的加速度計(J. H. Zhang, et al., “Flextensional fiber Bragg grating-based accelerometer for low frequency vibration measurement,” Chinese Optics Letters, vol. 9, Sep 2011.),其彈性元件為曲型梁,見圖10。
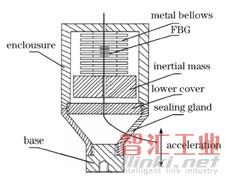
圖9 基于波紋管的加速度計
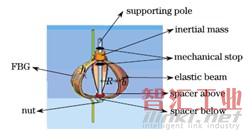
圖10 基于曲型梁的加速度計
丹麥的W. Yuan等報道了濕度不敏感的TOPAS聚合物光纖光柵(“Humidity insensitive TOPAS polymer fiber Bragg grating sensor,” Opt. Express, vol. 19, pp. 19731-19739, 2011.)。
其它方面簡述:
哈爾濱工程大學的J. Yang等人研究了低相干傳感系統中的高階干涉問題(“Higher-order interference of low-coherence optical fiber sensors,” Opt. Lett., vol. 36, pp. 3380-3382, 2011.)。研究指出,當傳感鏈上的傳感器數目較多時(比如10個),高階相干將成為降低信噪比的主要因素,這可通過降低各個傳感器的反射率加以抑制。這也是為什么采用FBG對進行傳感的系統中采用低反射FBG的原因。
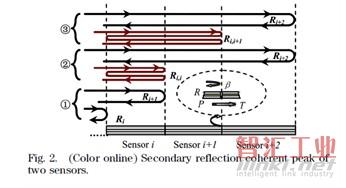
圖11 低相干傳感系統中的高階干涉
弗吉尼亞理工學院的D. Y. Wang等人提出了采用聲致rocking grating進行全光纖溫度傳感的方法(“Fully distributed fiber-optic temperature sensing using acoustically-induced rocking grating,” Opt. Lett., vol. 36, pp. 3392-3394, 2011.)。此前,該課題組曾經報道采用彎曲波產生長周期光纖光柵的方法(D. Y. Wang, Y. Wang, M. Han, J. Gong, and A. Wang, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 22, 1553, 2010)。此文與之不同的是采用PM光纖上產生扭轉波,利用溫度與雙折射的關系進行傳感。
臺灣的S. C. Her等報道了光纖傳感器的應變傳遞問題(“Effect of Coating on the Strain Transfer of Optical Fiber Sensors,” Sensors, vol. 11, pp. 6926-6941, Jul 2011.)。這方面的研究已經很多,可參考(1)X. Chang, et al., “Study on strain transfer of polymer optical fiber grating sensors,” in International Symposium on Photoelectronic Detection and Imaging 2009, SPIE vol 7381;(2)Ansari Farhad, Yuan Libo. “Mechanics of bond and interface shear transfer in optical fiber sensors. ”Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 1998, 124(4):385-394;(3)Zhou, G.; Li, H.; Ren, L.; Li, D. “Influencing parameters analysis of strain transfer in optic fiber bragg grating sensors.” SPIE Proc. 2006, 6179, 61790R1-9。
加拿大的M. T. V. Wylie等提出了一種分布式的位移傳感器(“Fiber Optic Distributed Differential Displacement Sensor,” JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, vol. 29, pp. 2847-2852, Sep 2011.)。
哈爾濱工程大學的Y.-b. Zhang等提出了利用法拉第鏡的偏振不敏感光纖傳感器(A polarization-insensitive fiber optic sensor based on Faraday rotator mirror. SPIE vol. 8191, 2011.),這種方法上個世紀就已經比較成熟。
英國南安普頓大學的G. Y. Chen等提出了基于微光纖的彈性碟片式加速度計(“Theoretical and experimental demonstrations of a microfiber-based flexural disc accelerometer,” Opt. Lett., vol. 36, pp. 3669-3671, 2011)。在傳感器結構方面相比于以前的設計并無創新之處,而新穎之處在于使用了microfiber。傳感器利用10 mm的microfiber達到了2.2rad/g的靈敏度。
美國伊利諾斯大學的Bassam等報道了利用光纖傳感器進行震后橋梁損傷評估的方法(“A simple quantitative approach for post earthquake damage assessment of flexure dominant reinforced concrete bridges,” Engineering Structures, vol. 33, pp. 3218-3225, 2011.)。
美國Redondo Optics, Inc.,公司的E. A. Mendoza等介紹了光纖氧傳感器在航空燃料箱內氣體環境監測方面的應用(Advances towards the qualification of an aircraft fuel tank inert environment fiber optic oxygen sensor system. SPIE vol. 8026: SPIE, 2011.)。
法國的C. Perrotton等綜述了光纖傳感器在氫氣泄露監測方面的應用(Review of optical fiber sensor technologies for hydrogen leak detection in hydrogen energy storage. SPIE vol. 8026: SPIE, 2011.)。
葡萄牙的H. Martins等報道了傳感用的不同結構的超長光纖拉曼激光器(“300 km-ultralong Raman fiber lasers using a distributed mirror for sensing applications,” Opt. Express, vol. 19, pp. 18149-18154, 2011.)。
(作者:張文濤)
(審核編輯: 智匯胡妮)
分享